| Analysis | Num par | Delta AIC | Adjusted ClusSize | Adjusted CS CV | N(indiv) | N(indiv) LCL | N(indiv) UCL | Bootstrap |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hn cos average group size | 2 | 22.4 | NA | NA | 31655 | 25889 | 38705 | |
| unif cos size regression | 2 | 24.9 | 6.3 | 0.026 | 26106 | 21665 | 31457 | |
| hr poly size regression | 2 | 23.7 | 6.1 | 0.026 | 27749 | 20917 | 36813 | |
| hn size bootstrap | 2 | 3.3 | 6.5 | 0.020 | 25449 | 22787 | 27868 | bootstrap |
| hr size bootstrap | 3 | 0.0 | 5.7 | 0.183 | 27704 | 23343 | 34598 | bootstrap |
| hr poly average size | 2 | 23.7 | NA | NA | 32673 | 24666 | 43278 | |
| hn cos group size regression | 2 | 22.4 | 6.2 | 0.026 | 27142 | 22150 | 33258 | |
| unif cos average size | 2 | 24.9 | NA | NA | 29858 | 24837 | 35893 |
Analysis of animals that occur in groups
Distance for Windows exercise Solution
Project Browser results
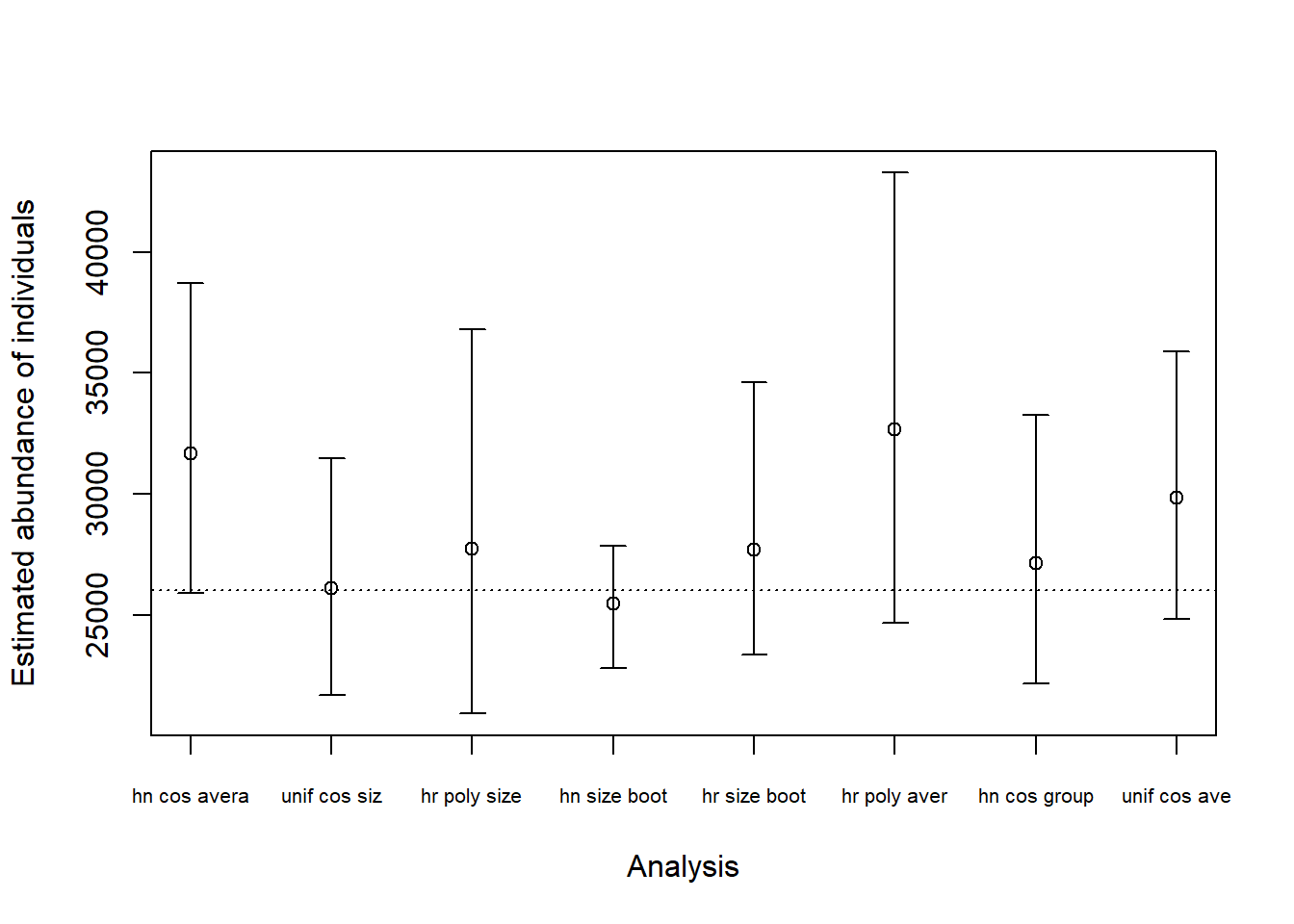
Below is an abbreviated set of Project Browser results of the 8 fitted models.
Striking features from the Results Browser is the strong preference (in \(\Delta\)AIC score) for models that contain cluster size in the detection function model. Contrast the adjusted cluster size estimates (whether by regression or by use of cluster size as a detection function covariate) with the average size of detected clusters of 7.2. Observe the knock-on effect of the estimate average group sizes upon the estimates of abundance of individuals.
Interval estimates of abundance
All confidence intervals for estimates of individual abundance include the true value, however, each of the estimates using the average cluster size of detected clusters as an estimate of average cluster size in the population are positively biased. Positively biased to the extent that the lower confidence limits only just include the true value of 26000.
For further experimentation
A DistWin project with the 8 completed analyses is available for download if you wish to further explore the data set and conduct additional analyses.